Exploring Open Banking in the GTA: Opportunities and Potential Risks


Open Banking is an emerging concept having the capacity to transform the financial landscape in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) and beyond. By allowing customers to share their financial data securely with third-party providers, Innovative financial services and solutions are made possible through open banking. In this article, we will explore the opportunities and potential risks associated with Open Banking in the GTA, shedding light on its implications for consumers, businesses, and the overall banking ecosystem.
Understanding Open Banking:
Definition and Fundamental Ideas:
- Open banking is the activity of securely exchanging financial information with approved third-party service providers.
- Customer permission, data protection, and interoperability between financial institutions and service providers are some of the fundamental tenets of Open Banking.
Opportunities of Open Banking in the GTA:
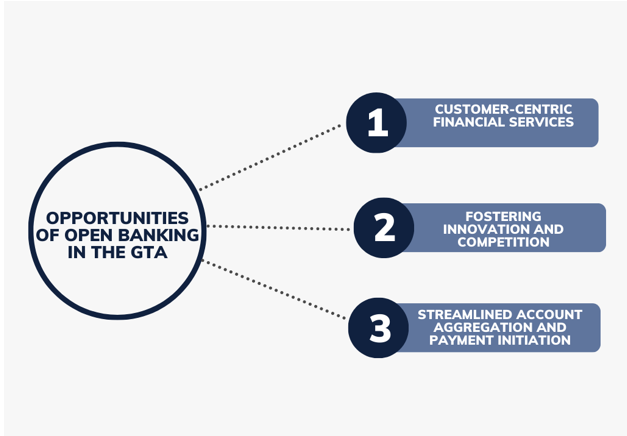

Customer-Centric Financial Services:
- Customers who may access and control their financial data from several suppliers through a single platform or application—known as open banking—are given greater authority.
- Customers may gain from individualized financial guidance, improved product suggestions, and solutions are created just for their needs.
Fostering Innovation and Competition:
- Opening up the financial industry to new companies and fintech businesses promotes innovation and competition.
- FinTechs may use consumer data to create cutting-edge products like budgeting applications, investing platforms, and loan comparison tools.
Streamlined Account Aggregation and Payment Initiation:
- Aggregating several bank accounts, credit cards, and financial accounts on one centralized platform is made easier by open banking.
- Payment initiation services make transactions quicker by enabling consumers to start payments straight from their bank accounts without the involvement of third person.
Potential Risks and Challenges:
Data Privacy and Security:
- Open Banking depends on the safe exchange of client financial data, which raises questions regarding data security and privacy.
- To maintain consumer confidence in the Open Banking environment; it is essential to protect their personal information against abuse, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
Regulatory Compliance:
- To safeguard customers, promote fair competition, and uphold the integrity of the financial system, the implementation of Open Banking needs a strong regulatory framework.
- Customer permission requirements, as well as rules governing data privacy (such as the Personal Information Privacy and Electronic Documents Act, or PIPEDA), must be complied with.
Customer Education and Trust:
- Customers may be apprehensive about disclosing their financial information to third-party providers since open banking is still a new idea.
- Customers must be informed about the advantages, dangers, and security precautions associated with Open Banking to foster confidence and promote adoption.
Ensuring a Secure Open Banking Environment:
Reliable Data Protection Measures:
- Strong security measures, such as encryption, access limits, and recurring security audits, must be put in place by financial institutions and service providers to safeguard consumer data.
- Data privacy can be supported by a framework that is provided by compliance with data protection laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Transparent Consent Mechanisms:
- To access and exchange financial data, Open Banking depends on client agreement.
- Customers must be aware of the extent of data sharing and have control over their information through clear and transparent permission processes.
Collaborative Partnerships:
Establishing standards, promoting best practices, and addressing difficulties in the Open Banking ecosystem need the development of cooperative collaborations between financial institutions, fintech firms, and regulators.
The Future of Open Banking in the GTA:
Financial Services Expansion:
The growth of financial services outside of traditional banking, such as individualized financial planning, investing platforms, and specialized loan solutions, is anticipated to be fueled by open banking.
Increased Collaboration and Partnerships:
- It is anticipated that financial institutions and fintech businesses will work together more closely to take advantage of Open Banking prospects and provide cutting-edge goods and services.
- To establish integrated client experiences, alliances with other sectors of the economy, including retail or healthcare, may potentially materialize.
Regulatory Developments:
- Regulatory frameworks will continue to evolve to handle the unique challenges and risks offered by Open Banking
- To ensure data privacy, security, and fair competition; authorities may establish regulations, standards, and supervision mechanisms.
Conclusion:
The Greater Toronto Area’s financial environment will benefit from exciting new prospects brought by open banking. Open Banking has the potential to improve the banking experience for people and companies in the Greater Toronto Area by adopting customer-centric services, encouraging innovation, and expediting financial transactions. Addressing possible hazards and difficulties is essential, though, as are issues with data privacy and security, regulatory compliance, and consumer education. The GTA can guarantee a safe and dependable Open Banking environment by establishing stringent data protection regulations, clear consent methods, and cooperative collaborations. To fully realize the promise of Open Banking and create a successful, customer-focused financial ecosystem in the Greater Toronto Area, stakeholders must collaborate.



